What is Cloud?
"The cloud" refers to servers that are accessed over the Internet, and the software and databases that run on those servers. Cloud servers are located in data centers all over the world.
Cloud is present in remote location = Data center = Infrastructure = Infrastructure contains server, storage, db's etc.
What is Cloud Computing?
Instead of doing computing on local machine / On premises. We will now doing computing in remote location i.e. cloud.
What is AWS?
AWS is a cloud provider, who provide Infrastructure as a service (IAAS).
It is a group of services, we will access through Amazon management console.
AWS has global infrastructure.
Deployment Models
Public Cloud: Provider's services which are access by everyone like AWS, Azure, GCP, Oracle.
Private Cloud: Provider's services which are accessed within the organization like Oracle.
Hybrid Cloud: Combination of public and private cloud is known as Hybrid cloud.
Service Models
- Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS)
IaaS contains the basic building blocks for cloud IT. It typically provides access to networking features, computers (virtual or on dedicated hardware), and data storage space. IaaS gives you the highest level of flexibility and management control over your IT resources.
AWS does not have any access inside our virtual machine.
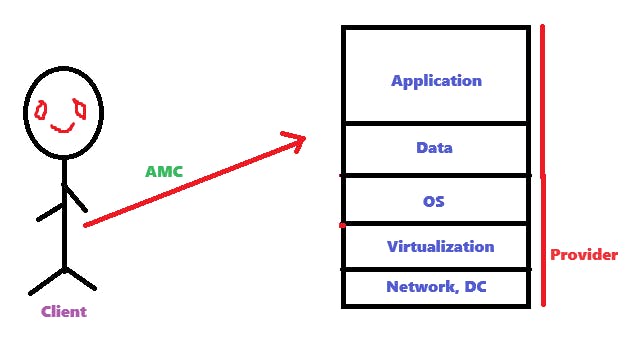
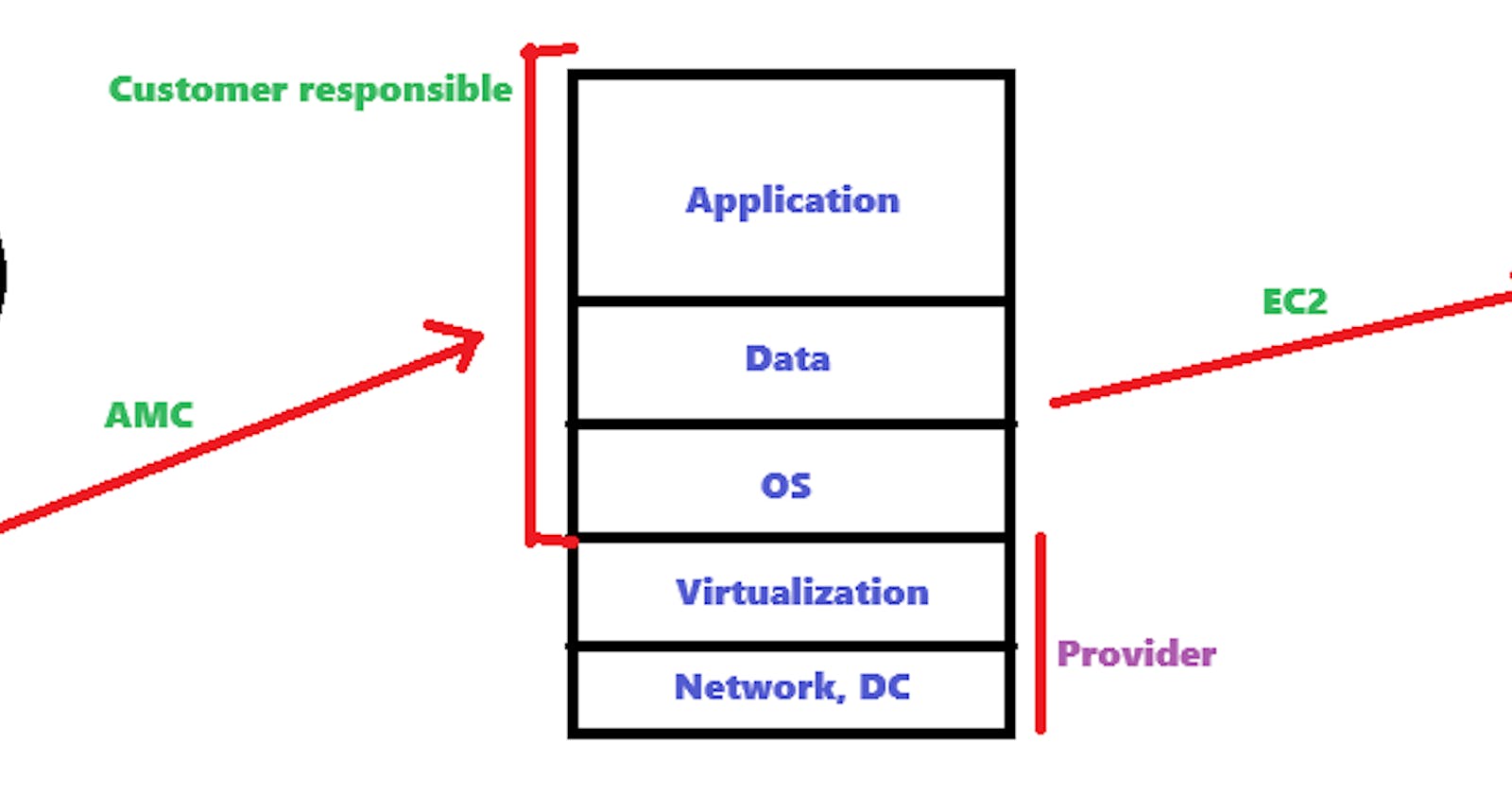
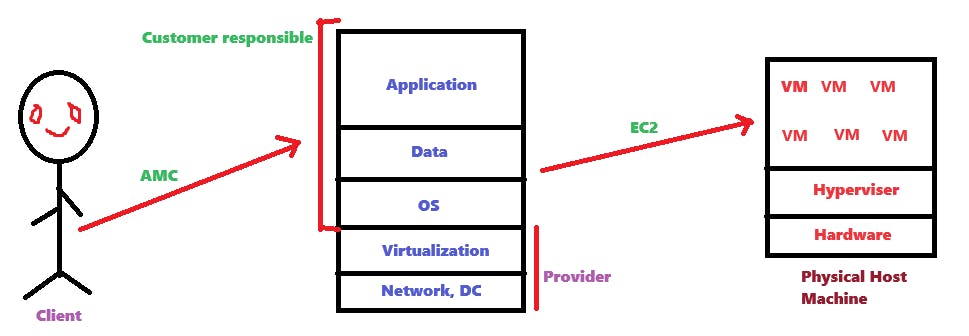
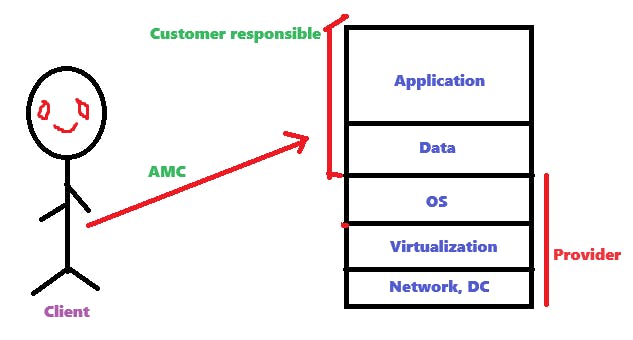
It is shared responsibility model.
Elastic compute cloud (EC2)
VM'S = Instances
EC2 is a web service where we can create a virtual machine.
Example: AWS
Platform as a Service (PAAS)
PaaS removes the need for you to manage underlying infrastructure (usually hardware and operating systems), and allows you to focus on the deployment and management of your applications. This helps you be more efficient as you don’t need to worry about resource procurement, capacity planning, software maintenance, patching, or any of the other undifferentiated heavy lifting involved in running your application.
No need to worry about the server, No control on server because server is controlled by the cloud provider.
Example: Azure
- Software as a Service (SAAS)
SaaS provides you with a complete product that is run and managed by the service provider. In most cases, people referring to SaaS are referring to end-user applications (such as web-based email). With a SaaS offering, you don’t have to think about how the service is maintained or how the underlying infrastructure is managed. You only need to think about how you will use that particular software.
Example: Gmail, Salesforce, Zoom etc.